You are given a list of non-negative integers, a1, a2, ..., an, and a target, S. Now you have 2 symbols+and-. For each integer, you should choose one from+and-as its new symbol.
Find out how many ways to assign symbols to make sum of integers equal to target S.
Example 1:
Input: nums is [1, 1, 1, 1, 1], S is 3.
Output: 5
Explanation:
-1+1+1+1+1 = 3
+1-1+1+1+1 = 3
+1+1-1+1+1 = 3
+1+1+1-1+1 = 3
+1+1+1+1-1 = 3
There are 5 ways to assign symbols to make the sum of nums be target 3.
Solution 1: Just do DFS and try both "+" and "-" at every position.
int result = 0;
public int findTargetSumWays(int[] nums, int S) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) return result;
helper(nums, S, 0, 0);
return result;
}
public void helper(int[] nums, int target, int pos, long eval){
if (pos == nums.length) {
if (target == eval) result++;
return;
}
helper(nums, target, pos + 1, eval + nums[pos]);
helper(nums, target, pos + 1, eval - nums[pos]);
}
Optimization: If the sum of all elements left is smaller than absolute value of target, there will be no answer following the current path. Thus we can return.
int result = 0;
public int findTargetSumWays(int[] nums, int S) {
if(nums == null || nums.length == 0) return result;
int n = nums.length;
int[] sums = new int[n];
sums[n - 1] = nums[n - 1];
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--)
sums[i] = sums[i + 1] + nums[i];
helper(nums, sums, S, 0);
return result;
}
public void helper(int[] nums, int[] sums, int target, int pos){
if(pos == nums.length){
if(target == 0) result++;
return;
}
if (sums[pos] < Math.abs(target)) return;
helper(nums, sums, target + nums[pos], pos + 1);
helper(nums, sums, target - nums[pos], pos + 1);
}
Solution 2: DFS,用hashmap存已计算过的结果,避免重复计算
public int findTargetSumWays(int[] nums, int S) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0){
return 0;
}
return helper(nums, 0, 0, S, new HashMap<>());
}
private int helper(int[] nums, int index, int sum, int S, Map<String, Integer> map){
String encodeString = index + "->" + sum;
if (map.containsKey(encodeString)){
return map.get(encodeString);
}
if (index == nums.length){
if (sum == S){
return 1;
}else {
return 0;
}
}
int curNum = nums[index];
int add = helper(nums, index + 1, sum - curNum, S, map);
int minus = helper(nums, index + 1, sum + curNum, S, map);
map.put(encodeString, add + minus);
return add + minus;
}
Solution 3: dp.先统计preSum,前几个数的组合就在-preSum ~ +preSum的范围,因为负数的存在,多设一维,正为0,负为1 。注意0的存在
public int findTargetSumWays(int[] nums, int S) {
if(nums == null || nums.length == 0){
return 0;
}
int n = nums.length;
int[] sum = new int[n + 1];
sum[1] = nums[0];
for(int i = 2; i < n + 1; i++){
sum[i] = sum[i - 1] + nums[i - 1];
}
// if(sum[n] == S || sum[n] == - S){ //错,因为0的存在,可以+-0
// return 1;
// }
if(S > 0 && sum[n] < S){
return 0;
}
if(S < 0 && sum[n] < - S){
return 0;
}
int[][][] dp = new int[n + 1][sum[n] + 1][2];
if(nums[0] == 0){ //把0当正数处理
dp[1][0][0] = 2;
} else{
dp[1][sum[1]][0] = 1;
dp[1][sum[1]][1] = 1;
}
for(int i = 2; i < dp.length; i++){
for(int j = 0; j <= sum[i - 1]; j++){
dp[i][j + nums[i - 1]][0] += dp[i - 1][j][0]; //j+nums[i-1],一定>0
dp[i][j + nums[i - 1]][1] += dp[i - 1][j][1]; //-(j+nums[i-1]),一定<0
if(j - nums[i - 1] >= 0){ //j-nums[i-1]
dp[i][j - nums[i - 1]][0] += dp[i - 1][j][0];
} else {
dp[i][nums[i - 1] - j][1] += dp[i - 1][j][0];
}
if(-j + nums[i - 1] >= 0){ //-j+nums[i-1]
dp[i][-j + nums[i - 1]][0] += dp[i - 1][j][1];
} else {
dp[i][-nums[i - 1] + j][1] += dp[i - 1][j][1];
}
}
}
if(S >= 0){
return dp[n][S][0];
} else{
return dp[n][- S][1];
}
}
Solution 4: 转化为subset sum。
The original problem statement is equivalent to: Find a subset ofnumsthat need to be positive, and the rest of them negative, such that the sum is equal totarget.LetPbe the positive subset andNbe the negative subset
For example:
Givennums = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]andtarget = 3then one possible solution is+1-2+3-4+5 = 3
Here positive subset isP = [1, 3, 5]and negative subset isN = [2, 4]
Then let's see how this can be converted to a subset sum problem:
sum(P) - sum(N) = target
sum(P) + sum(N) + sum(P) - sum(N) = target + sum(P) + sum(N)
2 * sum(P) = target + sum(nums)
So the original problem has been converted to a subset sum problem as follows:
Find a subsetPofnumssuch thatsum(P) = (target + sum(nums)) / 2
Note that the above formula has proved thattarget + sum(nums)must be even. We can use that fact to quickly identify inputs that do not have a solution.
public int findTargetSumWays(int[] nums, int s) {
int sum = 0;
for (int n : nums)
sum += n;
return sum < s || (s + sum) % 2 > 0 ? 0 : subsetSum(nums, (s + sum) >>> 1);
}
public int subsetSum(int[] nums, int s) {
int[] dp = new int[s + 1];
dp[0] = 1;
for (int n : nums)
for (int i = s; i >= n; i--)
dp[i] += dp[i - n];
return dp[s];
}
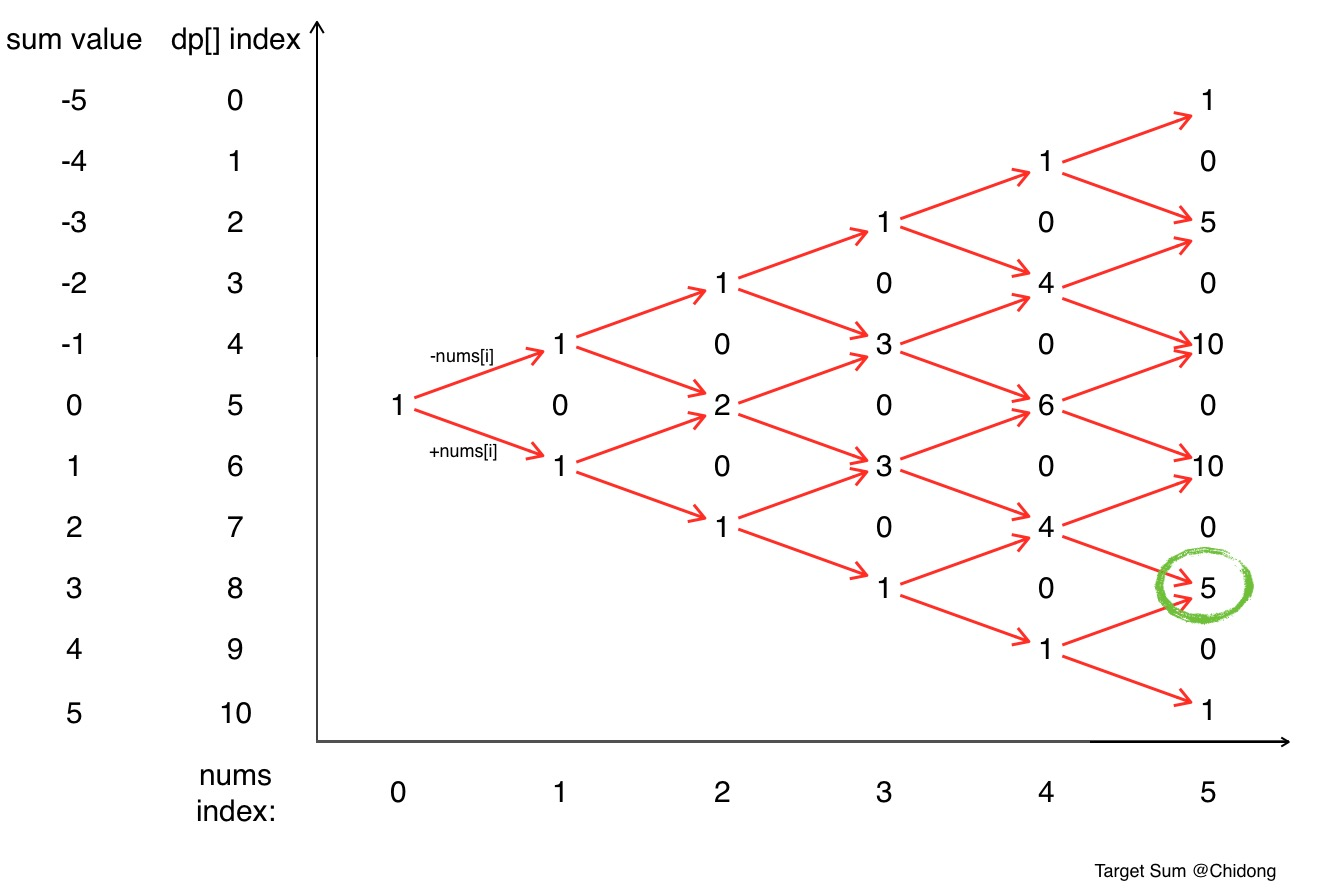
Solution 5: DP
public int findTargetSumWays(int[] nums, int s) {
int sum = 0;
for(int i: nums) sum+=i;
if(s>sum || s<-sum) return 0;
int[] dp = new int[2*sum+1];
dp[0+sum] = 1;
for(int i = 0; i<nums.length; i++){
int[] next = new int[2*sum+1];
for(int k = 0; k<2*sum+1; k++){
if(dp[k]!=0){
next[k + nums[i]] += dp[k];
next[k - nums[i]] += dp[k];
}
}
dp = next;
}
return dp[sum+s];
}